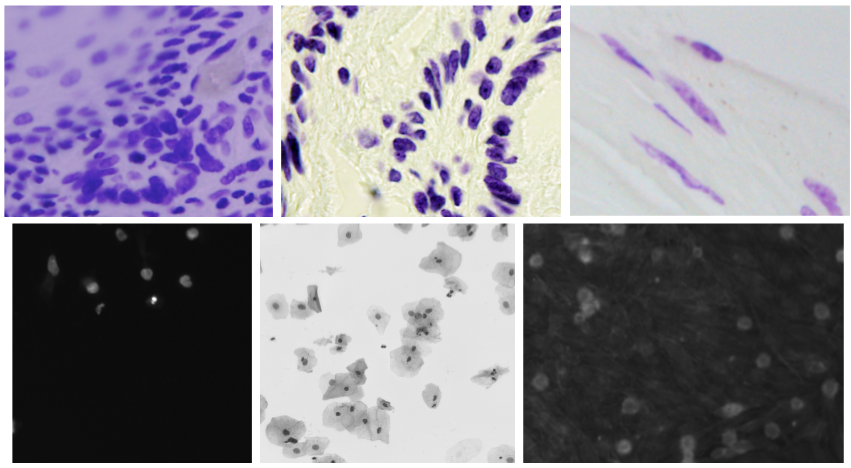
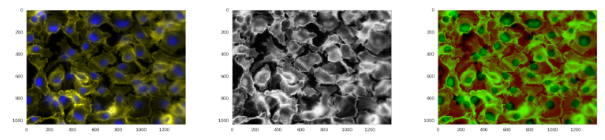
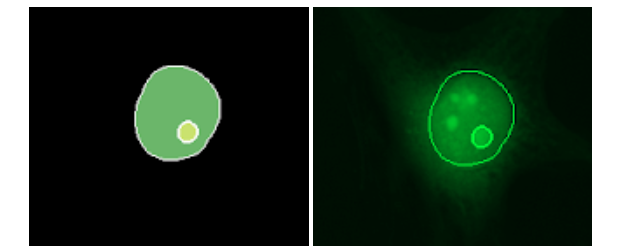
Ardigen AI Labs decided to participate in this competition; therefore, we formed a core team (Dawid Rymarczyk, Łukasz Maziarka, and Jan Kaczmarczyk, PhD), supported by the other data scientists from our company (Oleksandr Myronov, Bartosz Zieliński, PhD, Szymon Wojciechowski, and Michał Warchoł, PhD). In addition, we collaborated with the Academic Computer Center Cyfronet AGH for heavy GPU computations.
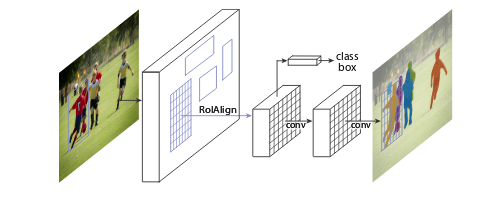
In the beginning, we focused on reviewing the state-of-the-art methods, and we concluded that the competition challenge could be addressed in two ways—using instance segmentation with heavy post processing or semantic segmentation. After a discussion, we decided to apply a Mask R-CNN model for this task. The model was developed by Facebook AI Research in 2017, and since then, it is a state-of-the-art method in semantic segmentation.
The Mask R-CNN model first generates a feature map from a backbone neural net, for example, Squeeze-and-Excitation ResNeXt (only convolutional layers are considered in the model because they provide a robust image representation). After extracting the feature map from the image, the model detects regions of interest (RoI), which are candidates for locations of objects (they are expressed in the form of coordinates of bounding boxes). In the next step, RoIs are filtered to remove those that overlap significantly, and then the remaining ones are classified as background or object. In the next step, each RoI goes through convolutional layers and at the end, there are three outputs: first for the bounding box of the object, second for the object’s class, and the third one for the segmentation. The segmentation output has fixed dimensions (e.g., 28 × 28 pixels) and therefore, needs to be resized to the original bounding box dimensions at the end of the pipeline.