In the field of neurodegenerative disease research, where every discovery can be a step towards a breakthrough, the role of technology —especially that which accelerates these studies— is becoming crucial. One area where this is particularly evident is in the analysis of brain slices, a fundamental aspect of understanding diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. This article takes a closer look at the latest AI advancements in brain slice segmentation, with a focus on SegGPT, an innovative tool that’s changing how researchers work. SegGPT isn’t just about doing things quicker; it’s about enabling image segmentation without extensive computer vision experience, potentially speeding up the process from lab findings to effective treatments.
Image Segmentation and Feature Extraction – Challenges and Solutions
In the research on neurodegenerative diseases, a common approach is to assess the treatment’s effectiveness by analyzing brain slices from treated subjects, often mice [1, 2]. To facilitate this assessment, it is highly desirable to automate two critical processes: image segmentation and feature extraction. Image segmentation entails selecting specific regions within an image for analysis, while feature extraction characterizes these chosen regions based on biologically relevant properties.
However, a robust 3D image segmentation method, known as atlas segmentation, is not suitable for 2D histopathological slides. This technique requires aligning a 2D image with a 3D atlas, a complex process that is still under development and thus has limitations.
There exist some AI solutions specific to neurodegenerative disease research, such as DeepSlice [3] and SeBRe [4]., However, despite their advancements, there are also specific constraints. DeepSlice is designed for aligning only coronally cut brain sections, ignoring other sectioning planes. On the other hand, SeBRe eliminates the need for image alignment by directly segmenting regions through an AI-integrated atlas, but this method is heavily dependent on extensive training data and faces challenges with the requirement for large amounts of labeled data.
Exploring the Few-Shot Segmentation Approach with SegGPT
Recently, a new approach to image segmentation has emerged, known as in-context image segmentation, or few-shot segmentation. This method involves providing an AI model with an example of the desired region for segmentation, and the model then attempts to segment previously unseen images based on this example.
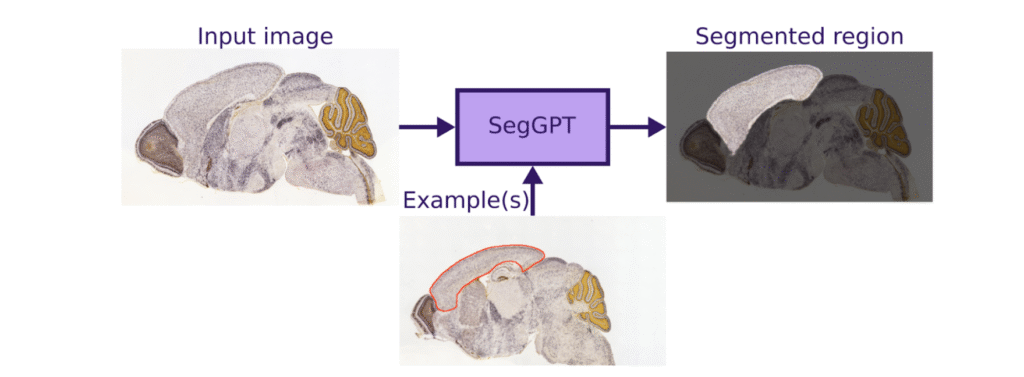
Fig. 1: SegGPT workflow: The model is provided with an example segmentation along with a new image, and it produces a similar segmentation for the new image
An interesting example of this approach is SegGPT [5], which can work with just a single labeled input (see Fig. 1). It’s important to realize that this method requires visually distinct segmented regions and may not perform well with vaguely visible areas, unlike atlas segmentation. However, it still offers a swift and automated means of selecting larger, distinctive objects.
For illustrative purposes, below are a few SegGPT examples of such segmentation, which were tested using open-source data from SeBRe’s work (Fig. 2).
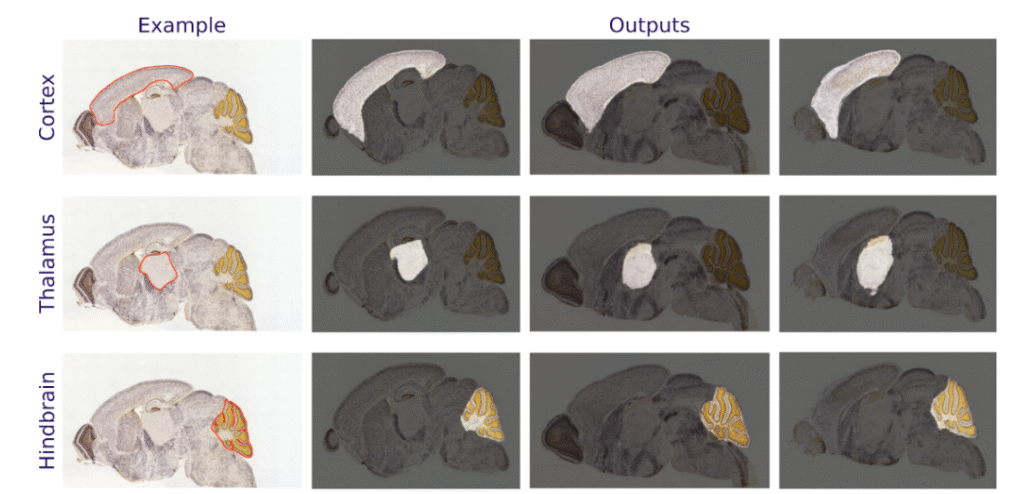
Fig. 2: SegGPT usage examples – segmentation of three distinctive brain regions (rows) in three new images (columns).
Feature Extraction Visualization – Broad, Adjustable Data for Tumor Identification
Once the region of interest has been automatically selected, we can proceed to extract biologically relevant properties (features) from that region (see Fig. 3). For instance, if we aim to quantify dark spots in the hindbrain region, we can utilize the previously generated hindbrain mask and focus our analysis there. Our initial step involves enhancing and labeling these dark spots to distinguish one from another.
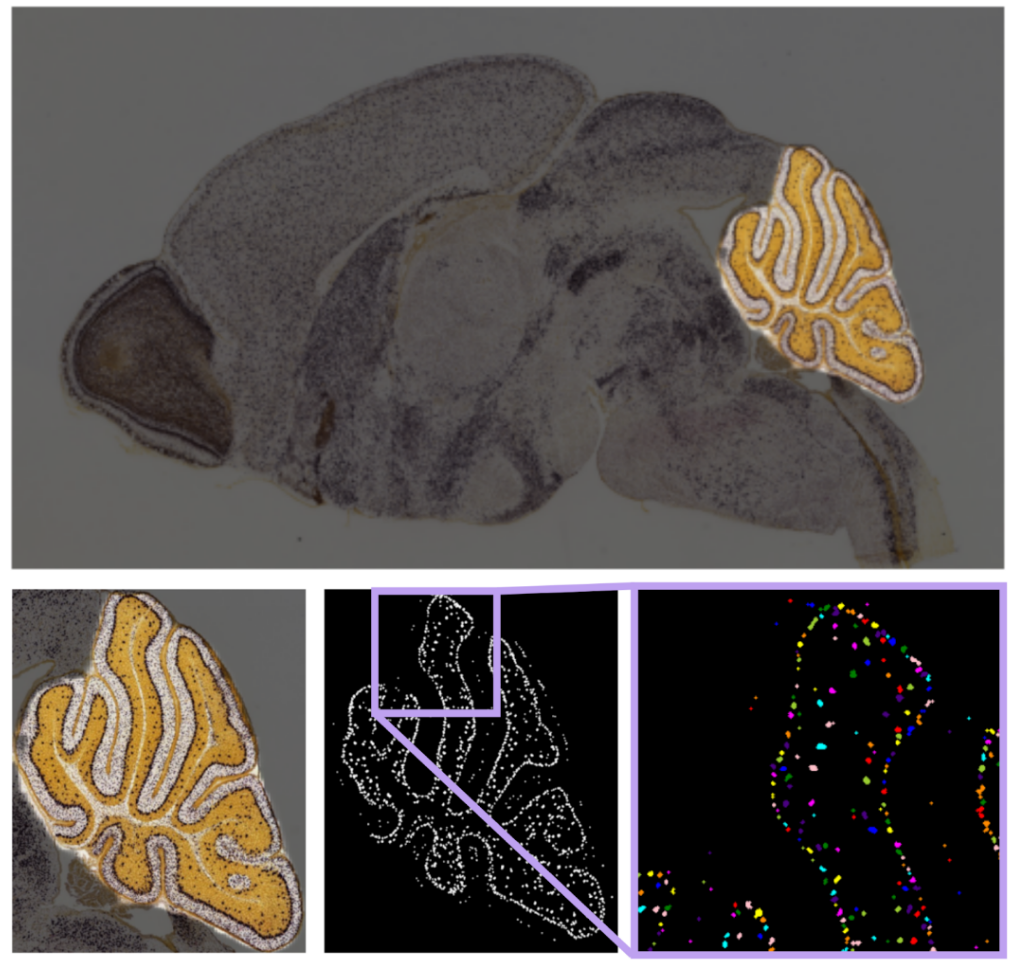
Fig. 3: Feature extraction visualization: The original image (top) is cropped to focus on the desired region (bottom left). Dots are enhanced during preprocessing (bottom center), and individual dots are distinguished for in-depth analysis (bottom right).
The analysis reveals the presence of 1311 dark spots. Below, you’ll find some of their mean parameters:

Additionally, here are the parameters of all dark spots considered as a single object:

Conclusion: Efficient Data Analysis with SegGPT and Feature Extraction
In summary, integrating innovative image segmentation techniques, such as SegGPT, and feature extraction methods allows for efficient analysis of biological data, particularly in the context of neurodegenerative disease research. Simplifying these complex processes and automating region selection leads to a faster and more thorough understanding of brain science research.
Works Cited:
[1] Cho, Seongeun, Andrew Wood, and Mark R. Bowlby. “Brain slices as models for neurodegenerative disease and screening platforms to identify novel therapeutics.” Current neuropharmacology 5.1 (2007): 19-33.
[2] Pieper, A. A., McKnight, S. L., & Ready, J. M. (2014). P7C3 and an unbiased approach to drug discovery for neurodegenerative diseases. Chem. Soc. Rev., 43(19), 6716–6726. doi:10.1039/c3cs60448a
[3] Carey, H., Pegios, M., Martin, L. et al. DeepSlice: rapid fully automatic registration of mouse brain imaging to a volumetric atlas. Nat Commun 14, 5884 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-41645-4
[4] Iqbal, A., Khan, R. & Karayannis, T. Developing a brain atlas through deep learning. Nat Mach Intell 1, 277–287 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s42256-019-0058-8
[5] Wang, Xinlong, et al. “Seggpt: Segmenting everything in context.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.03284 (2023).
Further Reading from Ardigen’s Knowledge Hub
Explore more AI and image analysis innovations in life sciences:




