Artificial intelligence - based screening: Accelerating binding receptor analysis in drug discovery
In the early stages of drug discovery, efficiently identifying and characterizing binder-receptor interactions is crucial for prioritizing viable candidates. Traditional wet-lab experiments, while effective, can be time-consuming and resource-intensive. This case study explores how a biotechnology client leveraged AI-driven computational techniques to streamline the evaluation process, enabling faster and more accurate identification of promising receptor targets while optimizing experimental efforts.
Challenge
A client in the biotechnology industry had identified a specific binder molecule and, through initial lab experiments, discovered that this binder could potentially interact with multiple receptors. The challenge was to efficiently evaluate all these potential interactions to identify the most probable receptor targets and understand the nature of these interactions, without resorting to extensive and time-consuming wet-lab experiments for each possibility.
Approach
The presented case study outlines a computational approach leveraging AI and molecular modeling techniques to address this challenge. The process began with predicting the 3D structures of the binder and the various receptor candidates. Following structure prediction, tools like MaSIF were employed to analyze the surface properties of these molecules, specifically focusing on potential binding hotspots. To further investigate the interactions, molecular docking simulations were performed to predict the binding poses and affinities between the binder and each receptor. Finally, Molecular Dynamics (MD) simulations were conducted on the docked complexes to refine the structural details and gain deeper insights into the stability and dynamics of the interactions.
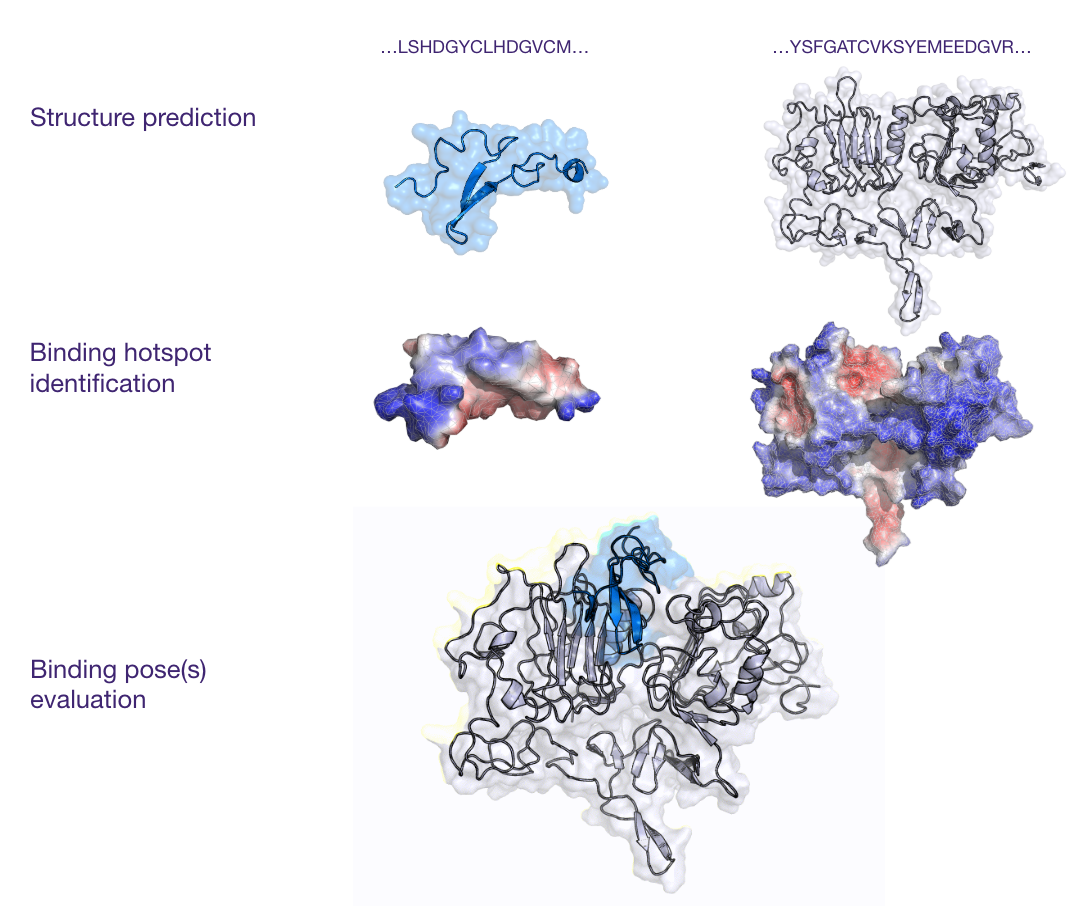
Results
- Reduced manual effort in screening
- Efficiently characterized multiple potential complexes in parallelI
- Identified most probable receptor, focusing wet-lab efforts
- Provided deep insights for potential binder modifications
By integrating AI-driven computational screening with molecular modeling techniques, this approach significantly enhanced the efficiency of evaluating binder-receptor interactions. The combination of structural prediction, molecular docking, and molecular dynamics simulations enabled rapid identification of the most promising receptor targets while minimizing reliance on time-consuming wet-lab experiments.
This streamlined process not only reduced manual effort but also provided deep insights into binding stability and potential optimizations for the binder molecule. As a result, the client was able to accelerate their drug discovery pipeline, focusing experimental resources on the most viable candidates.
Ultimately, this case study highlights the power of computational methods in modern drug discovery, demonstrating how AI and molecular simulations can drive smarter, faster, and more cost-effective decision-making.



