High-content screening (HSC) assays such as Cell Painting represent a rich data source for phenotypic drug discovery. Machine learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) methods for image-based profiling are enabling a new era in phenotypic drug discovery. In particular, introducing ML into your workflows enhances the quality of prediction through multimodal approaches. You can read more about this in our previous article: High Content Screening: Redefining What Is Possible with Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning.
Human-defined morphological features, such as size, shape, intensity, granularity, and texture, can be extracted from HCS data by using image analysis tools such as CellProfiler1. However, this can take hundreds of hours and may not be able to extract all the insights packed in the images. ML methods not only automate image analysis but also enable feature extraction that extends beyond human-defined morphological features.
In addition to the phenotypic features, chemical features of the tested compounds also provide a valuable source of data for predicting potential drug candidates. To empower researchers and accelerate phenotypic drug discovery, we have developed the Ardigen phenAID platform, a solution that introduces multimodal predictive capabilities to HSC image analysis.
Analyzing phenotypic and chemical features with Ardigen phenAID
Ardigen phenAID is an AI-powered platform that combines multiple modalities, such as image and chemical structure data, to enhance the quality of predictions. PhenAID enables automated extraction of diverse morphological features, together with the classification and clustering of cellular phenotypes to help identify potential drug candidates. In addition to extracting phenotypic insights from HCS data, phenAID incorporates information about the chemical structure of the screened compounds.
This multimodal approach provides powerful insights into the Mode of Action (MoA) and bioactivity property predictions. To show its effectiveness, we benchmarked this method using a validated, proprietary dataset from Merck containing thousands of compounds.
Ardigen phenAID platform applied to a proprietary dataset from Merck KGaA
In a pilot project with Merck, we applied the Ardigen phenAID platform to analyze one of their proprietary HSC datasets. The analysis consisted of two tasks: mode of action and bioactivity properties prediction. For each task, we assessed performance using one modality (image or chemical structures features) or multimodal approach (image and chemical structure features) with both human-defined and AI-based features.
For each input modality, we trained two models: one for MoA and one for bioactivity properties prediction. We compared AI-based features (extracted with image and molecule representation models) with human-defined descriptors (CellProfiler and ECFP for images and structures respectively). For both methods, we assessed the confidence of the predictive scores when using only one modality versus multimodal approaches.
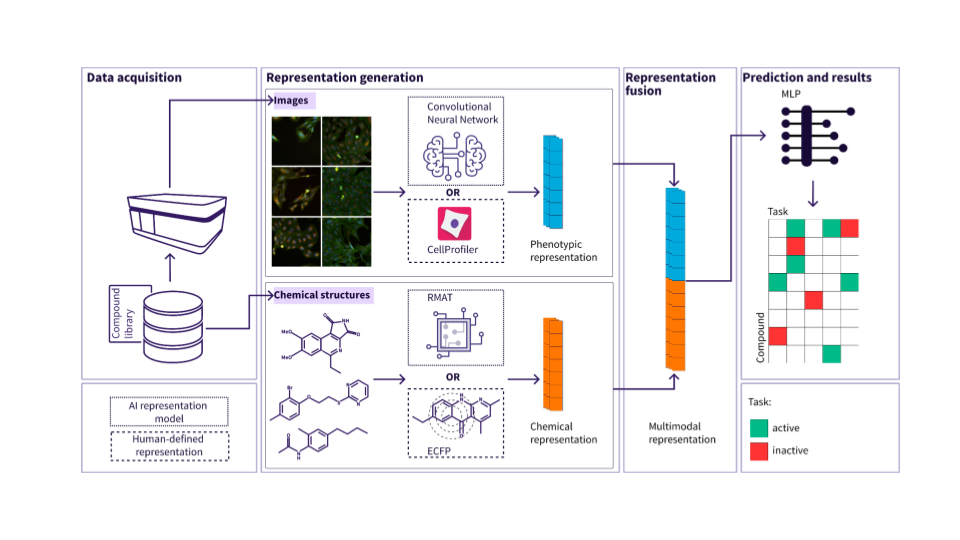
Figure 1. Method overview: Images and structures are processed using either AI model or human-defined features and passed through MLP to obtain predictions.
Multimodal approach boosts the accuracy of prediction
Works Cited:
- Stirling, D.R., et al. (2021). “CellProfiler 4: improvements in speed, utility and usability”, BMC Bioinformatics 22, 433. DOI: 10.1186/s12859-021-04344-9.
- Rumetshofer, E., et al. (2018). “Human-level protein localization with convolutional neural networks,” International conference on learning representations.
- Maziarka, Ł. et al. (2024). “Relative molecule self-attention transformer,” J Cheminform 16, 3. DOI: 10.1186/s13321-023-00789-7
- Rogers, D., and Hahn, M. (2010). “Extended-Connectivity Fingerprints”, J. Chem. Inf. Model. 50, 5, 742–754 DOI: 10.1021/ci100050t
The multimodal approach consistently improved the prediction scores across all tested setups. It enhanced both the Mode of Action and bioactivity property prediction on a diverse set of biological tasks (Table 1).
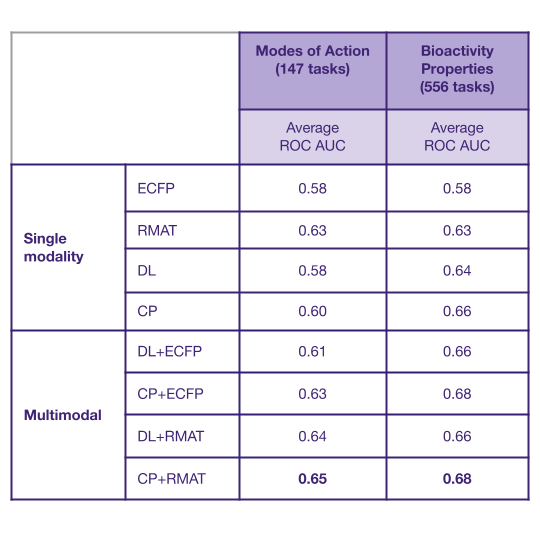
Table 1: A numerical comparison between modalities using ROC AUC scores. For AI-driven modalities, phenotypic representations were generated using a Deep Convolutional Neural Network (GapNet2) pre-trained using a compound-matching task (DL) and representations of chemical structures generated using a proprietary Relative Molecule Attention Transformer (RMAT3) model. Human-defined modalities were obtained using CellProfiler (CP1) for morphological features and Extended-Connectivity Fingerprints (ECFP4) for chemical structures. Bold values represent the best result.
Incorporating machine learning and AI solutions for extracting phenotypic features streamlines drug discovery efforts, reducing both the cost and time of analysis. Using deep learning and AI models, we could extract features faster and cheaper while retaining the prediction performance.
Through this study, we have demonstrated that multimodal approaches increase the confidence of predictions when it comes to HSC data analysis. By combining phenotypic features extracted from the images with chemical structures of the active molecules, we were able to enhance Mode of Action and bioactivity prediction for dozens of compounds tested by Merck KGaA.
To learn more about the results of this study, download our poster.
You can learn more about the phenAID platform here.
Further Reading from Ardigen’s Knowledge Hub
Explore more innovations in High Content Screening, AI, and phenotypic drug discovery:




